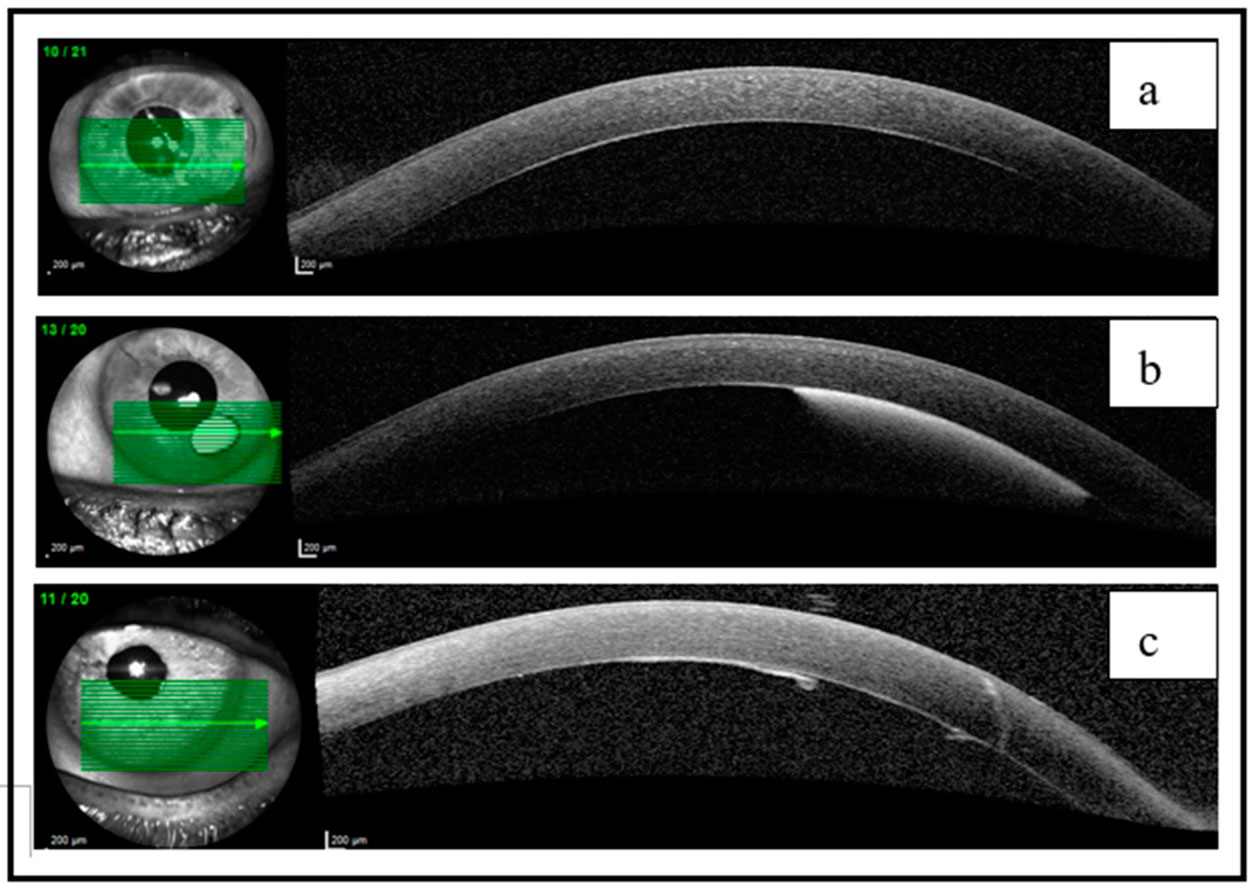
Treatment
Foods To Avoid
Latest
Recovery and Aftercare After Laser Treatment in Canada Proper recovery and aftercare after laser treatment…
Best Glaucoma Clinics in Vancouver When searching for the best glaucoma clinics in Vancouver, patients…
Best Glaucoma Clinics in Toronto When it comes to protecting your vision, finding the best…
Best Glaucoma Clinics in Canada When it comes to glaucoma treatment, Canada stands out for…
Canaloplasty Surgery in Australia Canaloplasty surgery in Australia has become one of the preferred options…
Viscocanalostomy Surgery in Australia Viscocanalostomy Surgery is a non-penetrating glaucoma procedure performed to reduce intraocular…
Cost Comparison: Laser vs. Eye Drops vs. Surgery in Australia For patients managing glaucoma, understanding…
Trabeculectomy Surgery in Australia Trabeculectomy surgery is one of the most common and effective treatments…