Common Drugs that Can Worsen Glaucoma
I. Introduction
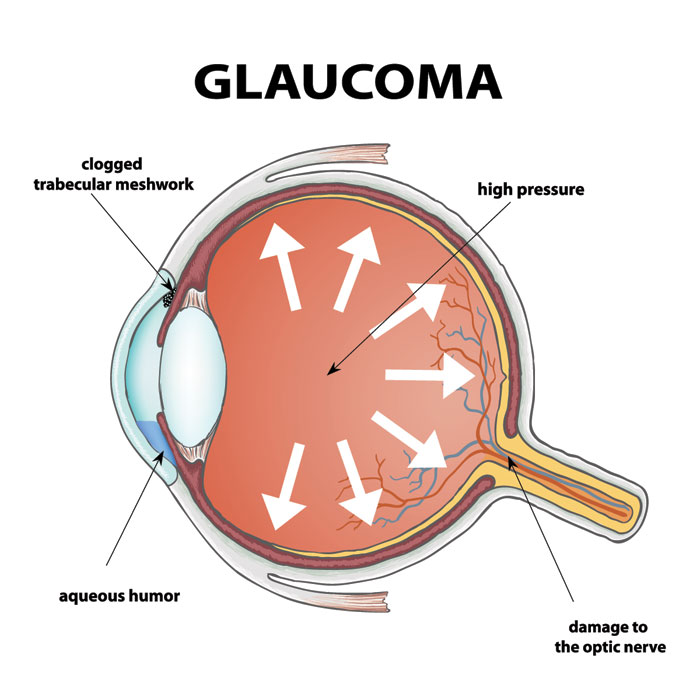
Glaucoma is a serious eye condition that can lead to vision loss if not properly managed. While most people focus on eye pressure control and regular check-ups, one important but often overlooked factor is medication use. Certain drugs can increase the risk of worsening glaucoma or trigger complications. Being aware of these medications is essential for anyone diagnosed with the condition.
II. Why Medications Matter in Glaucoma Management
The relationship between glaucoma and medications is complex. Some drugs can elevate intraocular pressure (IOP) or restrict fluid drainage in the eye, increasing the likelihood of optic nerve damage. Individuals with glaucoma—or those at high risk—must carefully review any medication they take to avoid complications.
III. Drugs That Can Worsen Glaucoma
Several types of medications can negatively affect glaucoma. Common categories include:
- Steroids: Corticosteroids, whether in eye drops, oral tablets, inhalers, or injections, can raise eye pressure when used for a long period.
- Antidepressants: Some antidepressants, especially tricyclic types and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can trigger angle-closure glaucoma in sensitive individuals.
- Blood Pressure Medications: While these control systemic blood pressure, certain medications may reduce blood flow to the optic nerve, increasing the risk of damage.
- Antihistamines and Decongestants: Commonly found in allergy and cold medicines, these can dilate the pupil and worsen narrow-angle glaucoma.
- Painkillers: Opioid-based pain medications, when taken in high doses or for extended periods, may influence eye pressure.
IV. Side Effects and Potential Risks
The effect of these drugs varies depending on dosage, duration, and individual health conditions. Steroids are particularly risky for long-term users, while antihistamines can cause sudden angle-closure attacks in vulnerable patients. Always discuss with your doctor before starting or stopping any medication, and never self-adjust prescriptions without professional guidance.
V. Communicating with Healthcare Providers
Transparency with your healthcare team is essential. Inform your ophthalmologist and prescribing doctor about your glaucoma history. This allows them to:
- Recommend safer alternatives when possible
- Adjust doses to minimize risks
- Schedule frequent eye pressure checks
VI. Tips for Managing Glaucoma and Medication Risks
Managing glaucoma isn’t only about taking prescribed eye drops. Consider these steps:
- Stay active with regular, moderate exercise to promote healthy blood circulation.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in leafy greens and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Limit caffeine, as it can temporarily raise eye pressure.
- Avoid drinking large amounts of water in one sitting to prevent pressure spikes.
- Keep up with scheduled eye exams and follow your treatment plan strictly.
VII. Conclusion
Understanding how medications affect glaucoma can prevent serious complications. Awareness, open communication with healthcare providers, and consistent eye care are key to protecting your vision. By staying informed and proactive, you can manage glaucoma effectively and maintain long-term eye health.