The Hidden Connection: Acute Emotional Stress and Intraocular Pressure
Introduction
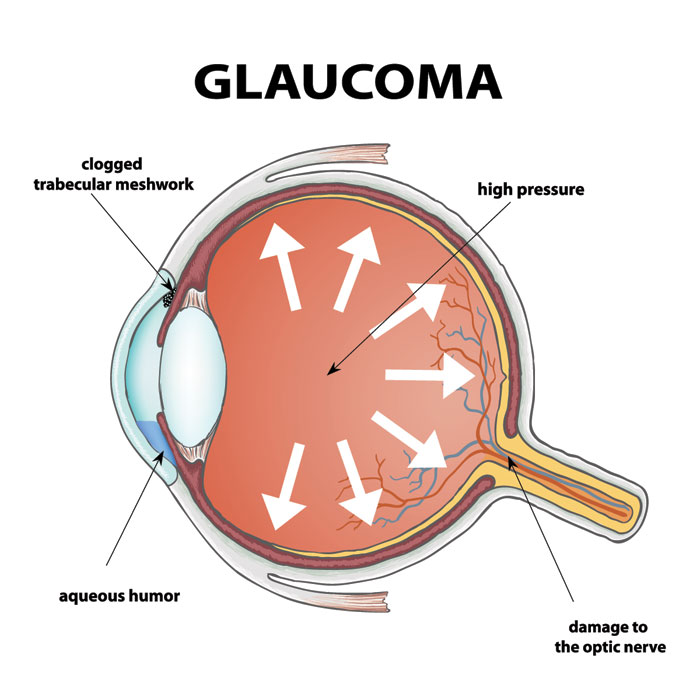
Intraocular pressure (IOP) plays a crucial role in maintaining eye structure and vision. Abnormal levels can lead to serious complications, including vision loss and conditions like glaucoma. Recent findings suggest that emotional stress—especially acute emotional stress—can significantly impact IOP levels. Understanding this relationship is key to protecting long-term eye health.
How Stress Influences Intraocular Pressure
The body’s stress response, also known as the “fight or flight” reaction, triggers hormonal changes that prepare you to face perceived threats. While this response is essential for survival, it can have unintended effects on eye pressure.
The Role of Stress Hormones
- Cortisol: Elevated cortisol levels can increase aqueous humor production while reducing its drainage, leading to higher eye pressure.
- Adrenaline: This stress hormone activates the sympathetic nervous system, which may alter ocular blood flow and contribute to IOP changes.
The autonomic nervous system, which includes both sympathetic and parasympathetic branches, further influences these changes. Stress tends to shift this balance, potentially causing temporary spikes in IOP.
Scientific Findings on Stress and Eye Pressure
Several studies confirm that acute stress can lead to short-term increases in intraocular pressure. Research highlights:
- Individuals under sudden emotional stress often experience noticeable fluctuations in IOP.
- People with pre-existing eye conditions, such as glaucoma, may be more sensitive to these changes.
- Stress management interventions have shown promise in stabilizing IOP levels.
Although more research is needed, these findings underscore the importance of stress control as part of overall eye care.
Real-Life Impact of Emotional Stress on Eye Health
Acute stress episodes—like a heated argument or unexpected emotional trauma—can trigger temporary spikes in eye pressure. While these fluctuations are often reversible, frequent or prolonged stress may contribute to cumulative damage over time. This risk is particularly concerning for individuals with conditions like ocular hypertension or glaucoma.
How to Manage Stress and Protect Your Eyes
Identify Stress Triggers
Being aware of what causes emotional stress is the first step toward effective management. Keep a stress journal or track symptoms like headaches, eye discomfort, or blurred vision during stressful periods.
Adopt Stress-Relief Practices
Incorporate relaxation techniques into your daily routine:
- Deep Breathing: Slows the heart rate and reduces stress hormone release.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Helps calm the nervous system and maintain emotional balance.
- Physical Activity: Activities like walking, yoga, or stretching can lower overall stress levels.
Consistency is key—regular practice can help reduce the likelihood of stress-induced IOP fluctuations.
Seek Professional Support When Needed
If stress becomes overwhelming or begins affecting your eye health, consult a healthcare professional. Regular IOP monitoring is also essential, especially for individuals with a history of eye pressure problems.
Conclusion
Acute emotional stress is more than just a mental health concern—it can influence intraocular pressure and impact long-term eye health. By understanding this connection and adopting proactive stress management strategies, you can help maintain stable IOP levels and protect your vision. Small changes in daily habits can make a big difference in overall eye health.