Impact of Sleep Patterns on Glaucoma: What You Need to Know
1. Introduction
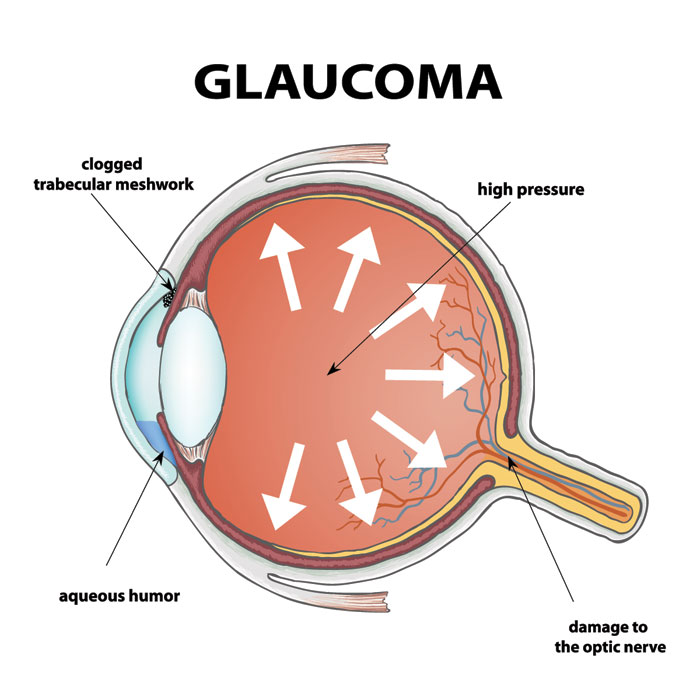
Glaucoma remains one of the leading causes of vision loss worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. While much attention is given to factors like intraocular pressure and genetics, recent studies reveal that sleep patterns may also play an important role in glaucoma development and progression. Understanding this connection can help individuals take steps to protect their vision and improve overall eye health.
2. The Role of Sleep in Overall Health
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining good health. It supports tissue repair, brain function, and hormonal balance. Sleep cycles include rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM stages, both crucial for physical and mental restoration. Disruptions in these cycles can lead to long-term health problems, and emerging evidence suggests that they may also influence eye pressure and optic nerve health.
3. How Sleep Patterns Influence Glaucoma
Researchers have found several ways in which poor sleep habits can affect glaucoma risk and progression:
- Sleep Duration: Individuals who sleep fewer than six hours per night face a higher risk of glaucoma. Interestingly, excessive sleep—more than ten hours per night—has also been linked to elevated risk, suggesting that both extremes can negatively impact eye health.
- Sleep Quality: Interrupted or poor-quality sleep can contribute to fluctuations in intraocular pressure, increasing the risk of optic nerve damage over time.
- Sleep Position: Certain positions, such as sleeping face down, can increase eye pressure during the night. Experts recommend side or back sleeping to help minimize this effect.
4. Tips for Improving Sleep and Supporting Eye Health
Developing healthy sleep habits may help reduce the risk of glaucoma complications and support overall well-being. Here are practical strategies to consider:
- Stick to a Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day to regulate your internal clock.
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Remove distractions like electronic devices and avoid bright lights before bedtime.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, or gentle stretching can reduce stress and prepare your body for restful sleep.
- Limit Stimulants: Reduce caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the evening, as they can disrupt sleep quality.
- Be Careful with Sleep Aids: Over-the-counter sleep aids or prescription medications should only be used under medical guidance to prevent unwanted side effects.
5. Conclusion
Sleep and eye health are closely connected. While more research is needed to fully understand this relationship, maintaining good sleep hygiene can be a simple yet effective way to support glaucoma management. Prioritize healthy sleep habits, schedule regular eye exams, and consult your eye care specialist for personalized advice.