The Most Accurate Test for Diagnosing Glaucoma: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Early detection of glaucoma can make a significant difference in preserving vision and preventing irreversible damage. Choosing the right diagnostic test is crucial because glaucoma often progresses silently, with no early warning signs. This guide explores the most accurate test for diagnosing glaucoma and provides insights into other commonly used examinations.
Common Tests for Glaucoma
Tonometry
Tonometry measures intraocular pressure (IOP), which is an important risk factor for glaucoma.
Pros: Quick, simple, and painless.
Cons: Not always reliable since eye pressure can fluctuate during the day.
Ophthalmoscopy
This test uses an ophthalmoscope to examine the optic nerve at the back of the eye.
Pros: Helps detect early optic nerve changes.
Cons: Subjective and requires an experienced specialist for accurate interpretation.
Perimetry
Also called a visual field test, perimetry checks your entire range of vision to identify blind spots that may indicate glaucoma.
Pros: Effective in detecting early vision loss patterns.
Cons: Time-consuming and often needs repeat testing for confirmation.
Additional Tests
Other examinations include pachymetry (measuring corneal thickness), gonioscopy (evaluating the drainage angle), and advanced imaging technologies for structural assessment.
The Most Accurate Test for Glaucoma
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Among the available methods, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) stands out as the most accurate diagnostic tool. This non-invasive imaging technique uses light waves to create detailed, three-dimensional scans of the retina and optic nerve, allowing specialists to detect even the smallest structural changes.
When OCT is Recommended
OCT is commonly advised for patients with risk factors such as elevated eye pressure or a family history of glaucoma. However, individuals with certain eye conditions like dense cataracts may need alternative tests.
Accuracy and Reliability
Clinical studies show OCT to be highly accurate, with detection rates between 90% and 95% for glaucomatous damage. This reliability makes it essential in both diagnosis and ongoing monitoring.
Cost details of laser glaucoma surgery in the Philippines
click here.
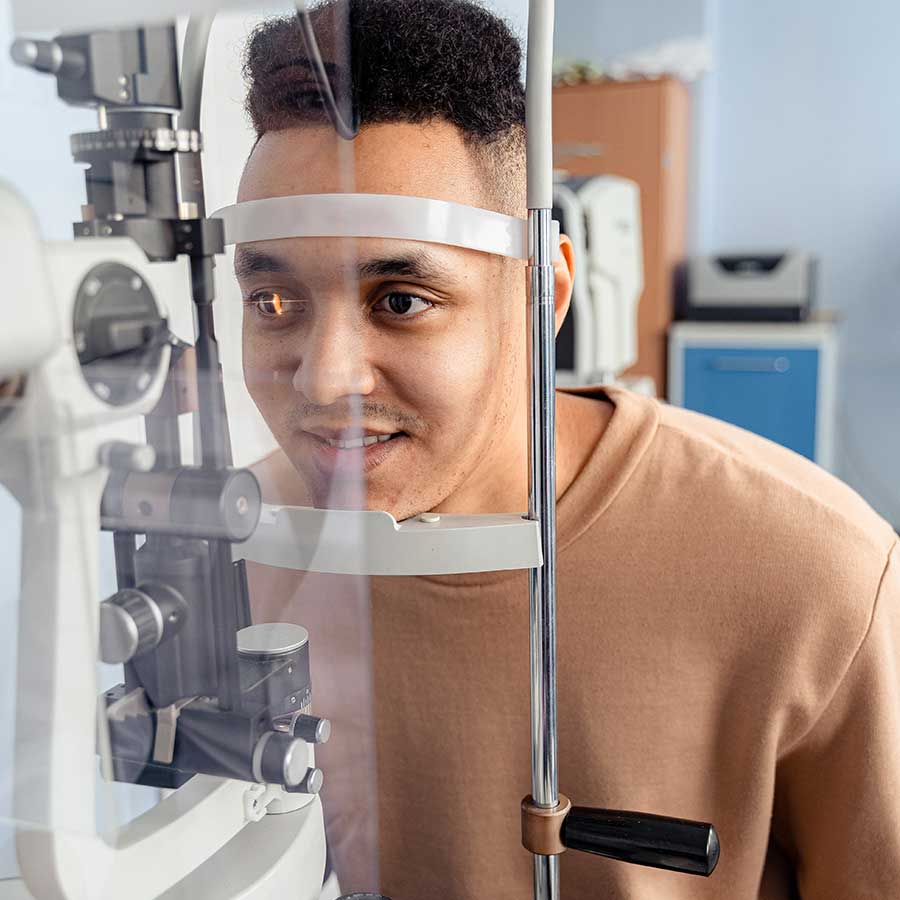
OCT Procedure: What to Expect
Preparation
Generally, no special preparation is needed. Your doctor may suggest dilating the pupils for clearer imaging.
During the Test
You’ll sit in front of the OCT scanner.
Your head will be stabilized with a chin and forehead rest.
A light beam scans your eye in seconds, capturing images without any discomfort.
The entire procedure usually takes 5–10 minutes.
After the Test
Your eye care professional will review the images, evaluate the optic nerve and retinal layers, and explain the findings to you.
Interpreting OCT Results and Next Steps
Understanding the Data
The OCT report shows images and graphs of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness. A significant thinning of this layer often signals glaucomatous damage.
Possible Results
Findings are generally classified as normal, borderline, or glaucomatous.
Follow-Up Care
Your doctor may recommend:
Regular OCT scans for monitoring progression.
Additional tests or medications.
Referral to a glaucoma specialist if needed.
Conclusion
OCT is one of the most accurate tools for detecting and tracking glaucoma. By combining this advanced test with regular eye exams, you can significantly reduce the risk of vision loss. Consult your eye care professional to determine the best screening and follow-up plan for your needs.