Beware of the Dangers: Unraveling the Risk Factors of Glaucoma Progression
Introduction
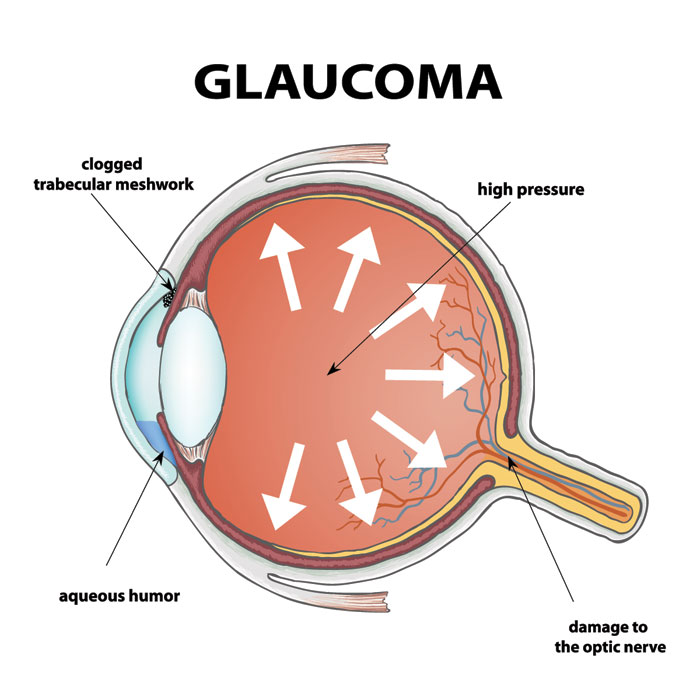
Glaucoma is a group of eye disorders that damage the optic nerve, responsible for transmitting visual information from the eyes to the brain. Without timely detection and treatment, glaucoma progression can lead to irreversible vision loss. Understanding the key risk factors is vital in preventing severe complications and protecting your vision.
The Progression of Glaucoma
Glaucoma develops gradually, with open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma as the two main types. Open-angle glaucoma progresses slowly, while closed-angle glaucoma can advance rapidly. In both cases, loss of peripheral vision often appears first, followed by increasingly limited vision, eventually leading to blindness if untreated.
Factors Affecting the Progression of Glaucoma
- Age
- The risk of glaucoma progression rises with age. It is most commonly diagnosed in individuals over 60, but younger people can also develop the condition.
- High Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
- Elevated intraocular pressure is a primary risk factor for glaucoma progression. Persistent high IOP can damage the optic nerve. Monitoring and controlling IOP through medications or other therapies is essential for preventing further complications.
- Race & Ethnicity
- Glaucoma risk varies among racial and ethnic groups. African Americans, Hispanics, and certain Asian populations have a higher likelihood of developing specific types of glaucoma.
- Family History
- Genetics can influence glaucoma development. Individuals with a family history of glaucoma may require more frequent eye examinations and early preventive care.
Understanding Glaucoma Stages
- Early stages (asymptomatic): Individuals may not notice symptoms. Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection.
- Mid-stages (mild symptoms): Mild signs may appear, such as difficulty adjusting to changes in light or gradual peripheral vision loss.
- Late stages (severe symptoms and vision loss): Advanced glaucoma can cause severe vision impairment or total blindness. Early intervention is critical to prevent irreversible damage.
Preventing Glaucoma Progression
- Regular Eye Exams
- Early detection is key. People over 40 should have comprehensive eye exams every two to four years, while those above 65 should undergo annual exams.
- Medication and Treatment
- Eye drops or oral medications help control IOP and slow glaucoma progression. In some cases, laser therapy or surgery may be required to manage the condition effectively.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle—including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management—supports eye health and can reduce the risk of glaucoma progression.
Recognizing the risk factors of glaucoma progression is essential for early detection and timely intervention. Proactive care through regular eye exams, appropriate medical treatment, and a healthy lifestyle can help preserve vision and reduce the likelihood of glaucoma-related complications.