Understanding Glaucoma: The Road to Blindness Explained
I. Introduction
Glaucoma is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness when left untreated. Early diagnosis and awareness are crucial to slowing down its progression and preserving vision. This article explains how glaucoma develops, its stages, and effective ways to prevent and manage the disease to protect your eyesight.
II. Common Types of Glaucoma
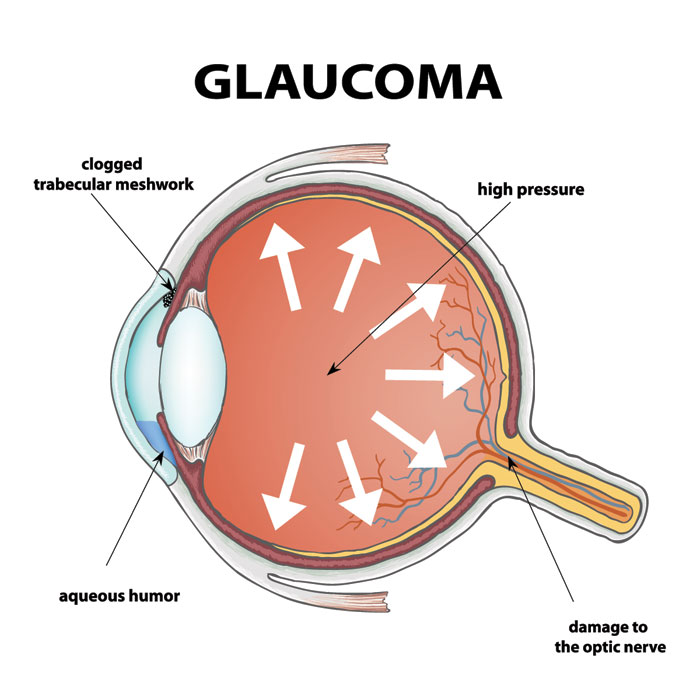
Glaucoma involves damage to the optic nerve, usually caused by increased eye pressure. This condition can lead to permanent vision loss. The two most common types are:
- Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG): The most common form, developing slowly over time. The drainage angle stays open, but the fluid drains poorly, raising pressure in the eye. POAG often has no symptoms early on, making early detection difficult.
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma: Occurs when the eye’s drainage angle becomes blocked, causing a sudden rise in eye pressure. This can be acute (sudden onset) or chronic (gradual onset). Symptoms include severe eye pain, blurred vision, and headache.
III. The Stages of Glaucoma
Understanding the stages of glaucoma helps track its progression:
1. Early Stage
- Mild damage to the optic nerve
- Small blind spots in peripheral vision
- Usually no noticeable symptoms
2. Moderate Stage
- More significant optic nerve damage
- Larger blind spots in vision
- Blurred vision or trouble with daily tasks
3. Advanced Stage
- Severe optic nerve damage
- Major loss of peripheral and central vision
- Difficulty recognizing faces and performing everyday activities
IV. Glaucoma Timeline
The time it takes for glaucoma to cause blindness varies. For untreated Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma, it can take 10 to 20 years or longer to progress to blindness. However, this timeline shortens dramatically without treatment or if other risk factors are present. Proper management and early treatment can significantly slow this progression.
V. Prevention and Treatment
While glaucoma cannot be completely prevented, timely action reduces its impact:
- Early Diagnosis: Regular eye exams, especially for those at higher risk—people over 40, those with a family history, or certain ethnic backgrounds—can detect glaucoma before vision loss occurs.
- Treatment Options:
- Prescription eye drops
- Oral medications
- Laser procedures
- Surgical treatments
- Lifestyle Support: While lifestyle changes cannot cure glaucoma, they can support eye health. Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, manage blood pressure, and reduce stress for overall well-being.
VI. Conclusion
Glaucoma can lead to blindness if ignored, but understanding its stages and acting early can save your vision. Schedule regular eye check-ups, be aware of risk factors, and commit to consistent treatment. If you experience vision changes or have a family history of glaucoma, seek professional advice immediately.