Introduction: The Optometrist’s Role in Glaucoma Care
Have you ever wondered how far an optometrist’s responsibilities go? Their work extends well beyond prescribing glasses or contact lenses. Optometrists play an essential role in safeguarding eye health, particularly in detecting serious conditions like glaucoma—a disease often called the “silent thief of sight” because it progresses without symptoms until it’s too late.
This article explores the critical part optometrists play in diagnosing glaucoma and why regular eye exams are more important than you might think.
What is Glaucoma?
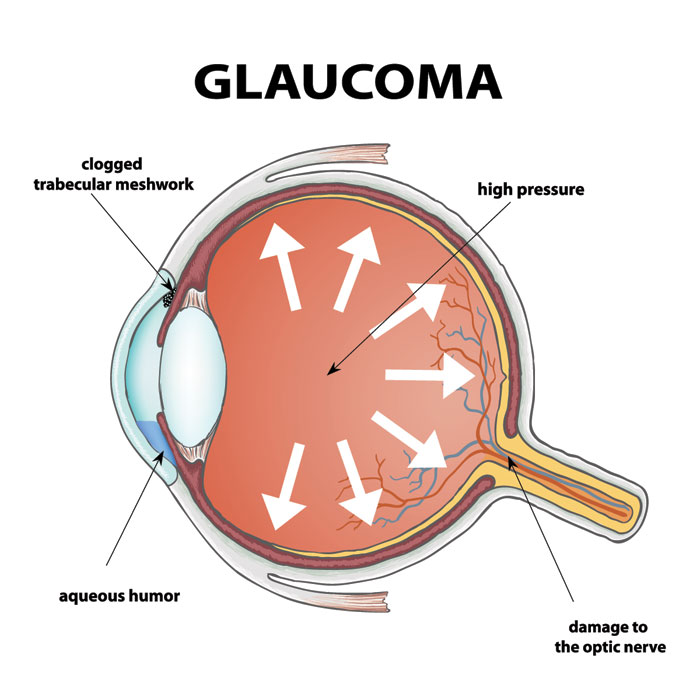
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, which is vital for vision. The primary cause is usually elevated intraocular pressure (IOP)—either because the eye produces too much fluid or the drainage system fails to work properly.
If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to irreversible vision loss or blindness. Early detection is the only way to prevent severe damage, as lost vision cannot be restored. Risk factors include:
Age (especially over 40)
Family history of glaucoma
High eye pressure
Medical conditions such as diabetes or hypertension
Race (higher risk among African and Asian populations)
The Role of an Optometrist in Eye Health
Optometrists are often the first point of contact for eye care. Their responsibilities include:
Conducting comprehensive eye exams
Measuring visual acuity and prescribing corrective lenses
Detecting and managing common eye conditions
Providing treatments such as vision therapy or low-vision rehabilitation
When it comes to glaucoma, optometrists are trained to recognize early warning signs—long before the patient notices any vision problems.
Can Optometrists Diagnose Glaucoma?
Yes, they can. Optometrists use several diagnostic tests to evaluate eye health, such as:
Tonometry: Measures eye pressure
Pachymetry: Determines corneal thickness
Ophthalmoscopy: Examines the optic nerve for damage
Visual Field Test: Checks for peripheral vision loss
By interpreting these results, an optometrist can detect glaucoma in its early stages. If the condition is suspected or confirmed, they can initiate treatment or refer the patient to an ophthalmologist for advanced care.
Optometrist vs. Ophthalmologist in Glaucoma Care
Both optometrists and ophthalmologists are vital in managing glaucoma, but their roles differ:
Optometrist: Focuses on eye exams, prescribing lenses, and diagnosing common eye diseases, including early glaucoma detection.
Ophthalmologist: A medical doctor who can perform eye surgeries, prescribe medication, and handle advanced or complicated cases of glaucoma.
In many cases, optometrists and ophthalmologists work together to ensure the best outcome for patients.
Why Regular Optometrist Visits Are Crucial
Glaucoma is often symptom-free in its early stages, which means vision loss can occur before you even realize something is wrong. Regular eye exams are your best defense. Experts recommend:
Annual check-ups for adults (especially after age 40)
More frequent exams if you have risk factors
Early detection significantly improves the chances of controlling glaucoma and preserving your vision.
Conclusion: Protect Your Eyes Today
Optometrists play a critical role in diagnosing glaucoma early, preventing irreversible damage. Prioritize routine eye exams, stay informed about your risk factors, and encourage others to do the same. Remember, protecting your vision starts with one simple step—booking that eye check-up.