I. Introduction
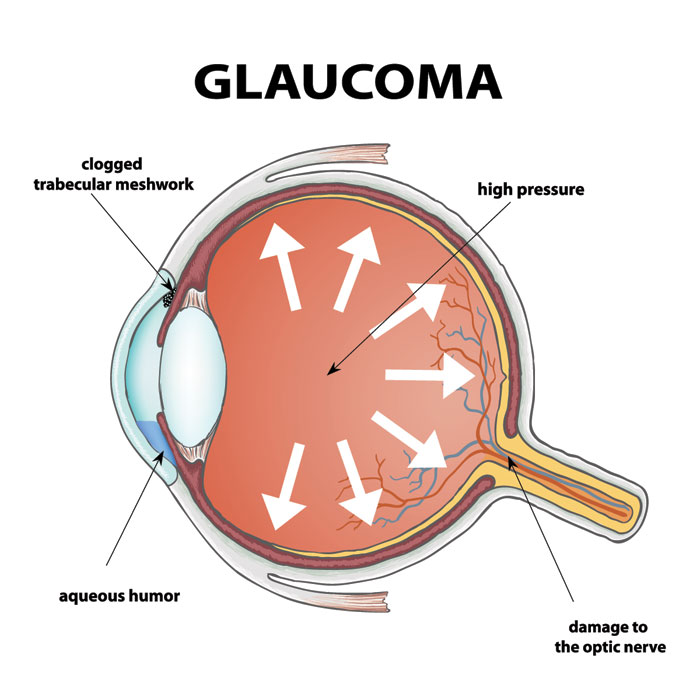
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, potentially leading to vision loss and blindness if left untreated. This damage often stems from increased intraocular pressure (IOP) caused by the abnormal buildup of fluid in the eye. Seeking an effective treatment plan is crucial in managing this condition and preserving your vision.
II. Understanding Glaucoma Oral Medications
While eye drops are the primary form of treatment for glaucoma, oral medications can also play a crucial role in reducing intraocular pressure. The most commonly prescribed oral medications for glaucoma include:
- Acetazolamide (Diamox)
- Methazolamide (Neptazane)
These medications belong to a class of drugs called carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. They aim to reduce the amount of fluid produced in the eyes, subsequently lowering IOP levels. Oral medications are typically reserved for more severe cases of glaucoma or when eye drops prove insufficient to effectively manage the condition.
However, just like any other medication, glaucoma oral drugs can also have side effects. Some commonly reported ones include fatigue, frequent urination, tingling sensations, gastrointestinal issues, and kidney stones. You should always consult with your healthcare provider regarding the potential side effects and risks before starting any medication.
III. Oral Medications vs Eye Drops
While oral medications have proven to be effective in treating glaucoma, they might not always be the preferred choice. Here\’s how they compare to eye drops:
Advantages of Oral Medications:
- Faster action in critical situations
- Suitable for severe cases where eye drops aren\’t sufficient
Disadvantages of Oral Medications:
- More side effects compared to eye drops
- Lower compliance due to the inconvenience of taking pills
Conversely, eye drops have fewer side effects and are generally more convenient to apply. However, both treatment options can be effective in managing glaucoma, and the ideal choice primarily depends on the severity of your condition and the doctor\’s recommendation.
IV. Alternatives to Glaucoma Oral Medications
Apart from oral medications and eye drops, there are other treatment options available for glaucoma, such as:
Laser Treatments:
Laser therapies aim to lower IOP by either increasing fluid drainage (selective laser trabeculoplasty, argon laser trabeculoplasty) or reducing fluid production (laser cyclophotocoagulation). These treatments can be less invasive and may serve as effective alternatives for people who cannot tolerate medication.
Surgical Procedures:
When medications and laser treatments aren\’t enough, surgical procedures like trabeculectomy or using drainage implants might be necessary. These procedures help enhance fluid drainage and provide long-term IOP control. It is crucial to discuss the benefits and risks of surgery with your eye care professional.
Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to medical interventions, some lifestyle changes can help manage glaucoma. These include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding excessive caffeine intake, and following a nutrient-rich diet.
V. Conclusion
Understanding glaucoma oral medication, its usage, benefits, disadvantages, and alternatives is vital in effectively managing the condition. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan tailored to your case. With the right approach, it is possible to preserve your vision and successfully manage glaucoma.