What to Look Out For: Recognizing the Symptoms of Glaucoma
Introduction
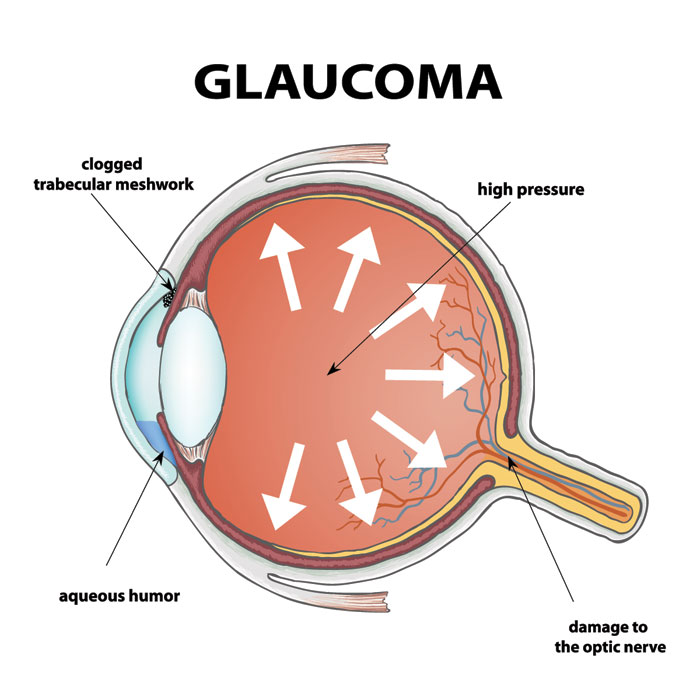
Glaucoma is a group of eye disorders that can gradually or suddenly damage the optic nerve, potentially leading to vision loss or even total blindness. Early detection and proper treatment can slow or prevent permanent damage. Understanding the symptoms of glaucoma is essential to recognize the condition early and seek timely medical care.
Common Symptoms of Glaucoma
The symptoms of glaucoma vary depending on its type and severity. Common signs include:
Redness of the Eye: Eyes may appear red or bloodshot due to increased intraocular pressure or inflammation.
Severe Eye Pain: Acute angle-closure glaucoma can cause intense eye pain as pressure rises rapidly.
Nausea and Vomiting: Rapid eye pressure increases may lead to nausea, vomiting, and severe pain.
Blurred or Distorted Vision: Difficulty focusing or distortion in the affected eye(s) is common.
Rainbow-Colored Halos Around Lights: Light may appear as halos due to high eye pressure affecting fluid refraction.
Rapid Vision Loss: In acute cases, vision can deteriorate suddenly.
Differences in Symptoms Based on Types of Glaucoma
Open-Angle Glaucoma
Gradual peripheral vision loss, often starting in one eye
Tunnel vision in advanced stages
Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Sudden eye pain, redness, and blurred vision
Severe headache, possibly extending beyond the affected eye
Rapid vision loss, a medical emergency
Normal-Tension Glaucoma
No unusual eye pain or redness
Difficulty seeing in low-light conditions
Significant optic nerve damage even with normal eye pressure
Risk Factors for Glaucoma
The likelihood of developing glaucoma increases with age, family history, certain medical conditions such as diabetes or hypertension, prior eye injuries, and ethnic background. Individuals in high-risk groups should prioritize regular eye exams and monitor any changes in vision.
Compare hospital rates for glaucoma surgery in the Philippines
What Happens If You Ignore These Symptoms?
Early detection is crucial for preventing permanent vision loss. Ignoring symptoms, delaying treatment, or skipping eye exams can result in irreversible damage or total blindness. Timely medical care can slow or halt disease progression, preserving both sight and quality of life.
When to Seek Medical Help
Acute angle-closure glaucoma requires immediate medical attention to prevent permanent damage within hours. Severe eye pain, sudden vision changes, or redness should prompt emergency care.
For other types, individuals at risk should maintain regular eye check-ups and consult their optometrist or ophthalmologist if symptoms persist or worsen.
Recognizing the symptoms of glaucoma is key to early intervention and effective management. Never ignore changes in your vision or eye health, and take proactive steps to protect your eyesight. Early care can make a significant difference in preventing long-term vision impairment.