Understanding Glaucoma: Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Introduction
Glaucoma is a serious eye condition and one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide. Recognizing its early symptoms can significantly impact the outcome of treatment. This guide outlines the warning signs, risk factors, and essential steps to protect your vision.
Why Glaucoma Demands Attention
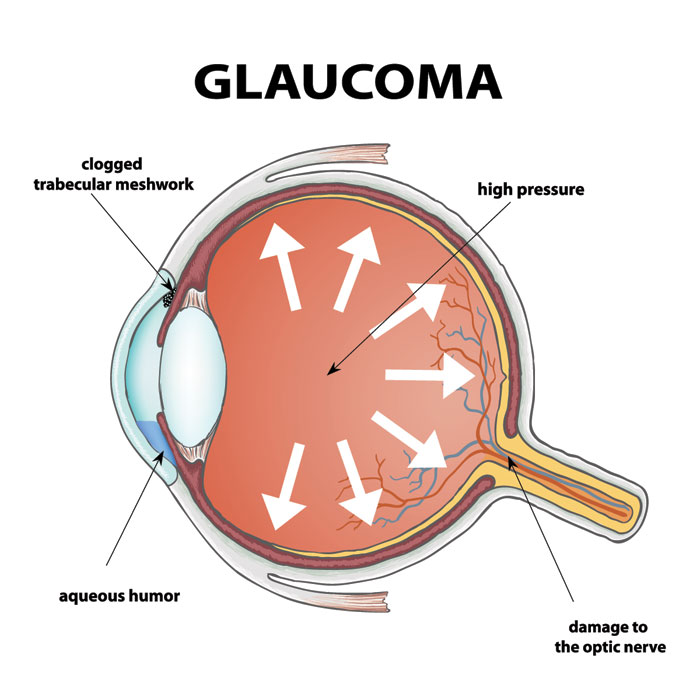
Glaucoma damages the optic nerve, which sends visual information from the eye to the brain. While it is commonly associated with high intraocular pressure, the condition can also occur with normal eye pressure. Several forms exist, including open-angle glaucoma, angle-closure glaucoma, normal-tension glaucoma, and childhood glaucoma. Each type may progress differently, but all pose a serious risk to eyesight.
Who Is at Risk?
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing glaucoma, such as:
- Age over 40
- Family history of glaucoma
- Medical conditions like diabetes or hypertension
- Thin corneas or severe nearsightedness
- Prolonged use of steroid medications
Understanding these risks can help prioritize regular eye examinations.
Warning Signs and Symptoms of Glaucoma
Glaucoma often develops silently, especially in its early stages. Common symptoms include:
- Blurred or hazy vision
- Severe eye pain or headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seeing halos or rainbow-colored rings around lights
- Sudden or gradual loss of peripheral vision, leading to tunnel vision
Open-angle glaucoma, the most common type, may not show noticeable symptoms until significant vision loss has occurred, making routine eye exams essential.
What to Do if You Notice Symptoms
If you experience any of these warning signs, consult an eye specialist immediately. Comprehensive eye exams often include:
- Measurement of intraocular pressure
- Evaluation of the optic nerve
- Visual field tests to assess peripheral vision
Treatment options vary but may involve prescription eye drops, oral medications, laser procedures, or surgery in severe cases.
Tips for Managing and Preventing Glaucoma Progression
Although glaucoma cannot always be prevented, early detection is key to controlling its impact. Helpful steps include:
- Regular eye exams, especially for those over 40 or with a family history of glaucoma
- Managing chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure
- Staying physically active to support overall eye health
Conclusion
Glaucoma often progresses without obvious signs, making awareness and regular eye checkups critical. Ignoring symptoms can lead to irreversible vision loss. Take proactive measures to safeguard your eyesight—early detection and timely treatment make all the difference.